A Kind of Nickel-base Corrosion Resistant and Heat Resistant Alloy -Nickel Alloy N06600

UNS N06600 is corrosion resistant to a wide range of corrosive media. The chromium composition gives the alloy better corrosion resistance under oxidizing conditions than nickel 99.2 (alloy 200) and nickel 99.2 (alloy 201, low carbon). Also, the higher nickel content gives the alloy good corrosion resistance under reducing conditions and in alkaline solutions, and is effective in preventing chloride-iron stress corrosion cracking. alloy 600 has good corrosion resistance in organic acids such as acetic acid, acetic acid, anthranilic acid, and stearic acid, and moderate corrosion resistance in inorganic acids. It has excellent corrosion resistance in high-purity water used in primary and secondary cycles in nuclear reactors. 600 is particularly outstanding in its ability to resist corrosion by dry chlorine gas and hydrogen chloride, with application temperatures up to 650℃. At high temperatures, the alloy in the annealed and solution-treated states has excellent resistance to oxidation spalling and high strength in air. The alloy is also resistant to ammonia and nitriding and carburizing atmospheres, but it is subject to corrosion by partially oxidizing media (e.g., green death fluids) when redox conditions change alternately.
Product characteristics
Alloy 600 has the following properties:
1. Excellent resistance to corrosion by reducing, oxidizing and nitriding media
2. Good resistance to stress corrosion cracking at both room and high temperatures
3. Good resistance to dry chlorine and hydrogen chloride gas corrosion
4. Good mechanical properties under fog, room temperature and high temperature
5. Good creep fracture strength, recommended for use in working environments above 700 "C.
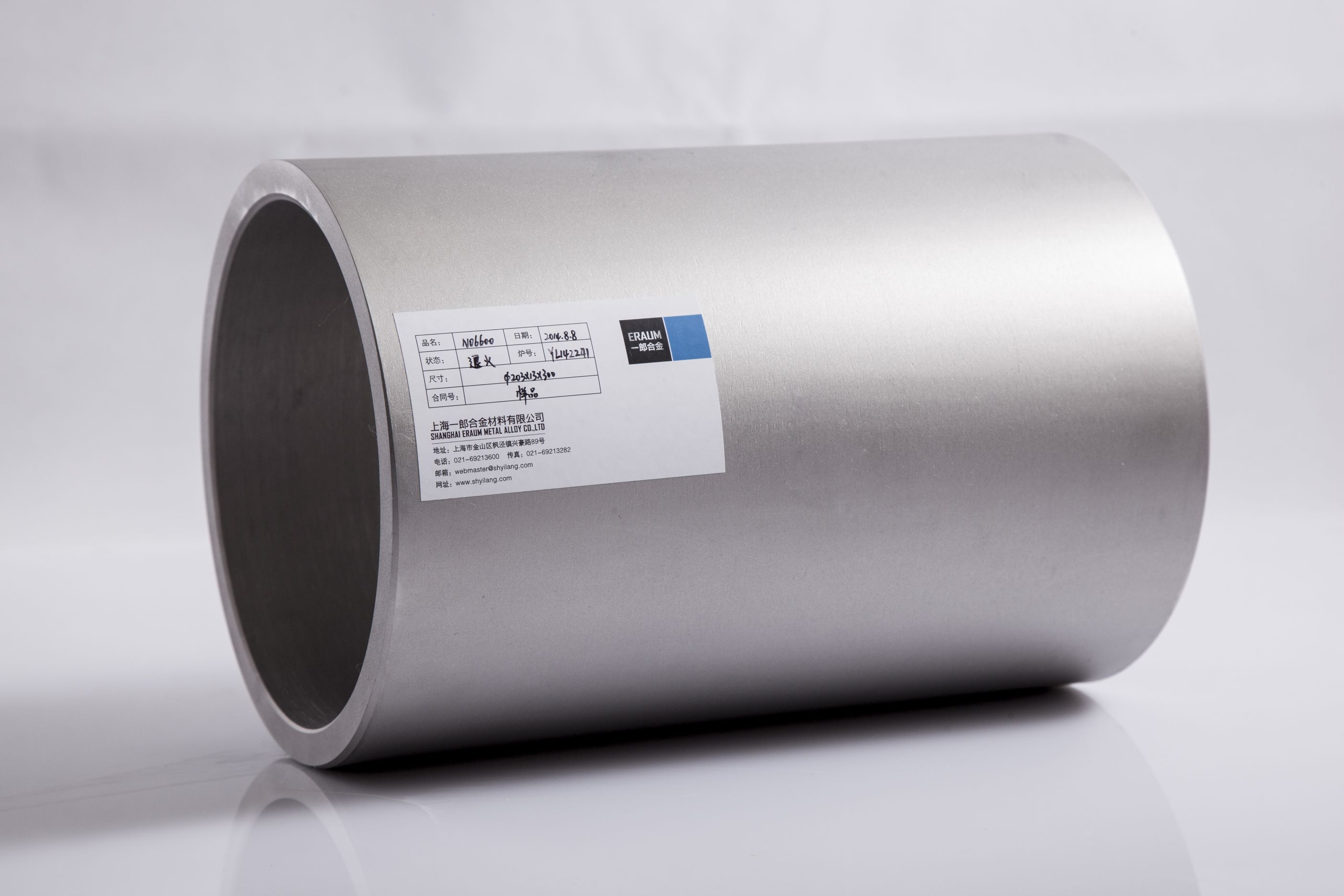

Metallographic structure
Alloy 600 is face-centered cubic lattice structure
Chemical Composition
% | Ni | Cr | Fe | C | Mn | Si | S | Cu | P | |
Alloy 600 | min | 72.0 | 14.0 | 6.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
max | - | 17.0 | 10.0 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.015 | 0.50 | 0.015 |
Nickel Alloy 600 Application Areas
1. Thermocouple sleeves in aggressive atmosphere
2. Vinyl chloride monomer production: resistance to chlorine hydrogen chloride, oxidation and carbonation corrosion
3. Uranium oxidation conversion to hexafluoride: resistance to hydrogen fluoride corrosion
4. Corrosive alkali metal production and use areas, especially the use of sulfide environment
5. Titanium dioxide production by chlorine gas method
6. Production of organic or inorganic chlorides and fluorides: resistance to chlorine and fluorine corrosion
7. Nuclear reactors
8. Heat treatment furnace in the curved neck bottle and parts, especially in the carbonization and nitriding atmosphere

Corrosion resistance
Alloy 600 is resistant to all kinds of corrosive media. The chromium composition gives the alloy better corrosion resistance than nickel 99.2 (alloy 200) and nickel 99.2 (alloy 201, low carbon) under oxidizing conditions. Also, the higher nickel content gives the alloy good corrosion resistance under reducing conditions and in alkaline solutions, and effectively prevents chloride-iron stress corrosion cracking.
Alloy 600 has good corrosion resistance in organic acids such as acetic acid, acetic acid, anthranilic acid and stearic acid, and moderate corrosion resistance in inorganic acids. It has excellent corrosion resistance in high purity water used in primary and secondary cycles in nuclear reactors.600 is particularly outstanding in its resistance to dry chlorine gas and hydrogen chloride, with applications up to 650C. At high temperatures, the alloy in the annealed and solution-treated states has excellent resistance to oxidation spalling and high strength in air. The alloy is also resistant to ammonia and nitriding and carburizing atmospheres, but it is subject to corrosion by partially oxidizing media (e.g., green death fluids) when redox conditions alternate

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
