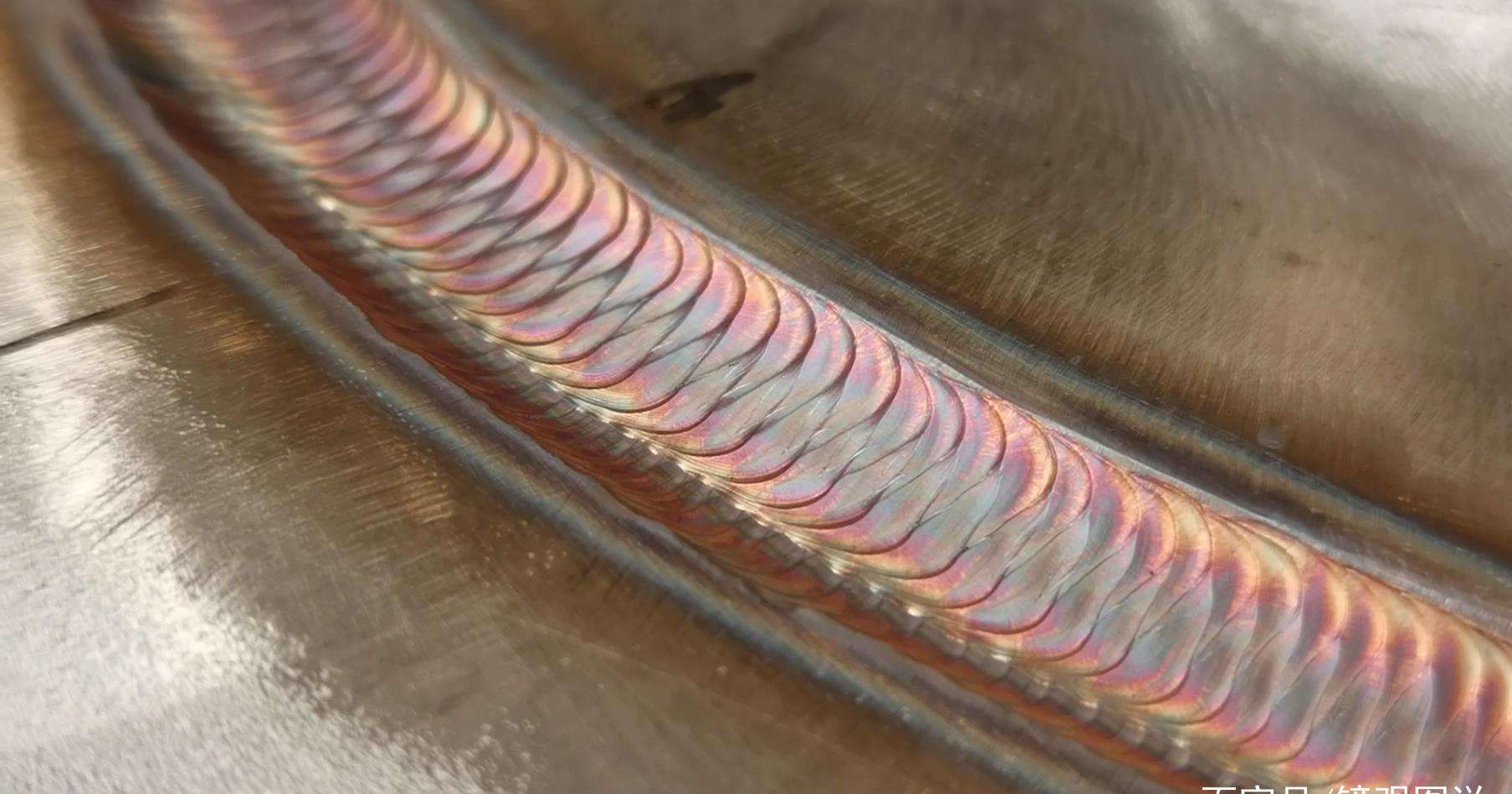
Bad Welding? Let's See What Factors Affect It
Weldability of metal materials refers to the ability of metal materials to obtain excellent welded joints under certain welding processes, including welding methods, welding materials, welding specifications and welding structure forms. If a metal can use more common and simple welding processes to obtain excellent welded joints, it is considered that this metal has good welding performance. The weldability of metal materials is generally divided into process weldability and service weldability.
Process Weldability: Refers to the ability to obtain excellent and defect free welded joints under certain welding process conditions. It is not the inherent property of metal, but the evaluation according to a certain welding method and specific process measures. Therefore, the process weldability of metal materials is closely related to the welding process.
Service Weldability: Refers to the degree to which the welded joint or the whole structure meets the service performance specified in the product technical conditions. The service performance depends on the working conditions of the welded structure and the technical requirements put forward in the design. It usually includes mechanical properties, low temperature toughness, brittle fracture resistance, high temperature creep, fatigue properties, endurance strength, corrosion resistance and wear resistance. For example, the commonly used s30403 and s31603 stainless steels have excellent corrosion resistance, and 16MnDR and 09MnNiDR low-temperature steels also have good low-temperature toughness.

Factors affecting the weldability of metal materials
1. Material Factors
Materials include base metal and welding materials. Under the same welding conditions, the main factors determining the weldability of base metal are its own physical properties and chemical composition.
Physical properties: such as melting point, thermal conductivity, coefficient of linear expansion, density, heat capacity and other factors of metal affect the processes of thermal cycle, melting, crystallization and phase transformation, so as to affect the weldability. Stainless steel and other materials with low thermal conductivity have large temperature gradient, high residual stress and large deformation during welding.
In terms of chemical composition, the most influential element is carbon, that is, the amount of carbon in the metal determines its weldability. Most of the other alloying elements in steel are also not conducive to welding, but their influence is generally much smaller than that of carbon. With the increase of carbon content in steel, the hardening tendency increases and the plasticity decreases, which is easy to produce welding cracks.
2 .Process Factors
Process factors include welding method, welding process parameters, welding sequence, preheating, post heat and post weld heat treatment. Welding methods have a great influence on weldability, mainly in two aspects: heat source characteristics and protection conditions.
By adjusting welding process parameters, taking other process measures such as preheating, post heating, multi-layer welding and controlling interlayer temperature, the welding thermal cycle can be adjusted and controlled, so as to change the weldability of metal. If measures such as preheating before welding or post welding heat treatment are taken, it is entirely possible to obtain welded joints without crack defects and meeting the service performance requirements.

3. Structural Factors
It mainly refers to the design form of welding structure and welded joint, such as the influence of structural shape, size, thickness, joint groove form, weld arrangement and section shape on weldability. Its influence is mainly reflected in heat transfer and force state. Different plate thickness, joint form or groove shape have different heat transfer velocity direction and heat transfer velocity, which affect the crystallization direction and grain growth of molten pool.
4. Service Conditions
It refers to the working temperature, load conditions and working medium of the welded structure during service. These working environment and operating conditions require the welded structure to have corresponding service performance. The more severe the service conditions are, the higher the quality requirements for welded joints are, and the more difficult it is to ensure the weldability of materials.


 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
