Do you know the Forging Technology?
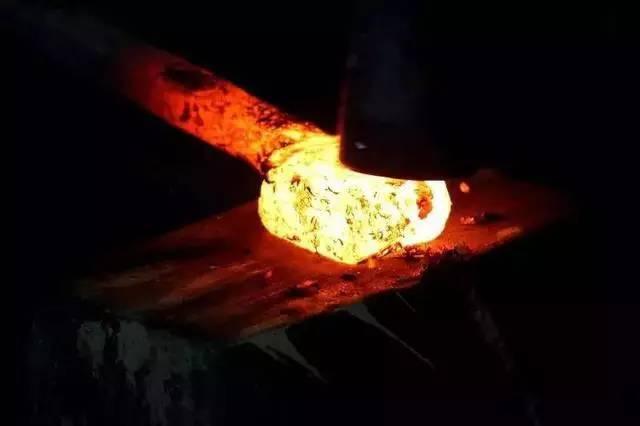
Before the Industrial Revolution, forging was the most common metal processing technology, such as horseshoe, cold weapons and armor, which were manually forged by blacksmiths from all over the world (commonly known as beating iron). He quenched the metal by repeatedly heating and hammering until he got the desired shape.

Process Cost: Mold Cost (Medium-High), Single Part Cost (Medium)
Typical products: hand tools, armor, vehicles, aerospace, heavy-duty machinery, etc.
Suitable output: single piece and small batch
Quality: Excellent particle structure greatly increases workpiece strength
Speed: Single piece time is usually less than 1 minute, depending on size, shape and material selection.

Applicable Material
1. Particularly suitable for ferrous metals (ferrous metals), such as alloys and stainless steels.
2. Some non-ferrous metals, such as titanium, copper and aluminium
Design considerations
1. The wall thickness of forged workpiece should be controlled at 5 mm-250 mm (0.2-9.84 in)
2. The reference weight of forged workpiece is between 0.25kg (0.55lb) - 60kg (132lb).
3. Part error: the error of small parts is 1 mm (0.04in), and that of large parts is 5 mm (0.2in).
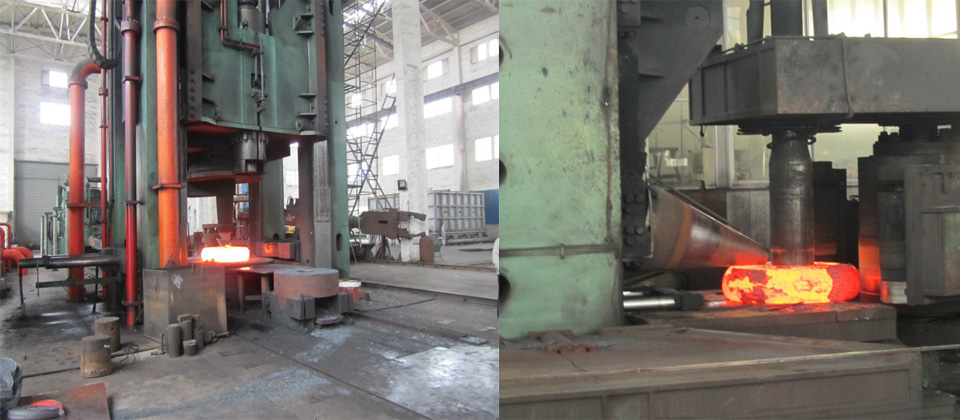

Detailed description of process
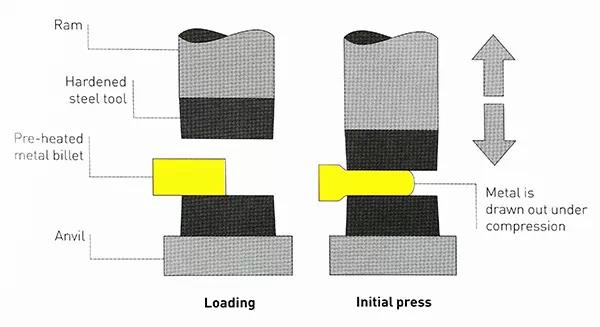
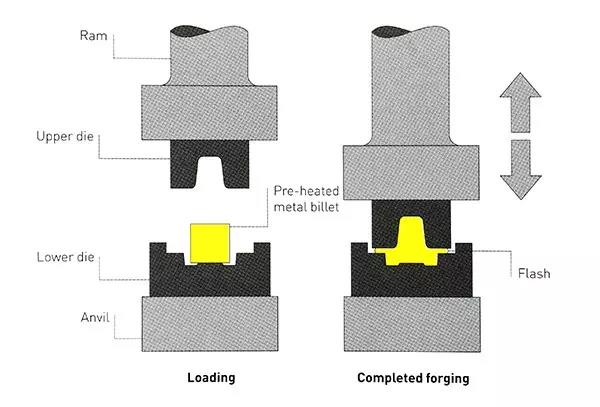
Opening and closing die forging: Heated metal blocks (yellow parts) are hammered by upper and lower dies to extend the shape of the metal. They must be manually operated by experienced operators.

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
