What impact will be on steel for different carbon content?
Carbon steel is divided into:
①Mild steel with carbon content less than 0.25%;
② Medium carbon steel with carbon content of 0.25% ~ 0.6%;
③ High carbon steel with carbon content greater than 0.6%.
Mild steel is a carbon steel with carbon content less than 0.25%. It is also called mild steel because of its low strength and low hardness. It includes most ordinary carbon structural steels and some high-quality carbon structural steels. Most of them are used for engineering structural parts without heat treatment, and some are used for mechanical parts requiring wear resistance after carburization and other heat treatment.
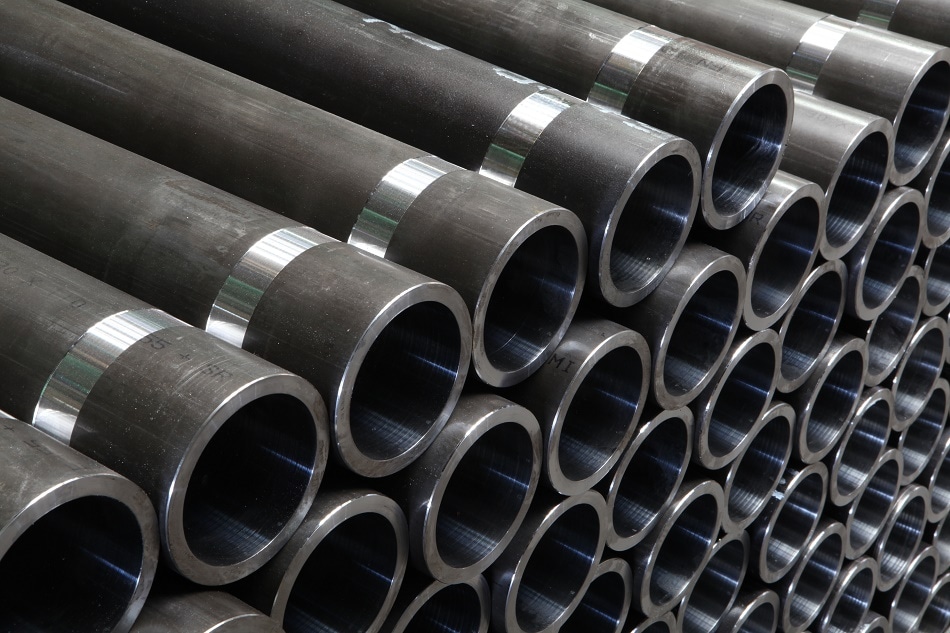

Medium carbon steel has good hot working and cutting performance and poor welding performance. The strength and hardness are higher than those of Mild steel, while the plasticity and toughness are lower than those of Mild steel. Cold rolled and cold drawn materials can be directly used without heat treatment, and can also be used after heat treatment. The quenched and tempered medium carbon steel has good comprehensive mechanical properties. The maximum hardness that can be achieved is about HRC55 (hb538), σ B is 600 ~ 1100mpa. Therefore, medium carbon steel is the most widely used in various applications with medium strength level. In addition to being used as building materials, it is also widely used to manufacture various mechanical parts.
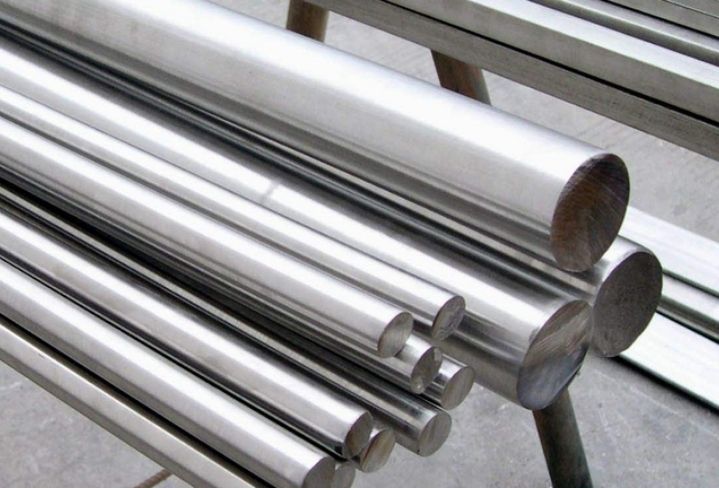

High carbon steel is often called tool steel, with carbon content ranging from 0.60% to 1.70%, which can be quenched and tempered, and poor welding performance. Hammer, crowbar, etc. are made of steel with carbon content of 0.75%; Cutting tools such as drills, taps and reamers are made of steel with a carbon content of 0.90% to 1.00%.


 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
