What production process is used for MTSCO welded pipes?
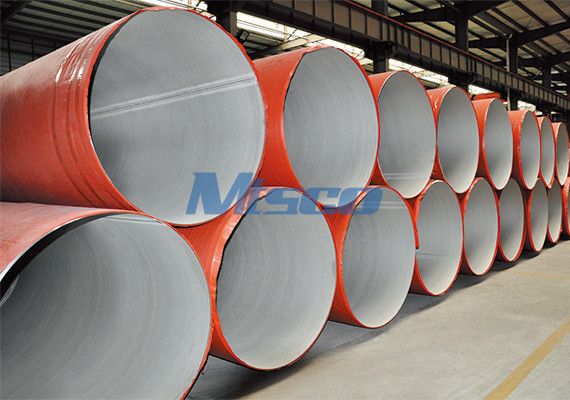

The welded pipe production process is a complex blend of technology and technical expertise that transforms raw materials into high-quality steel pipes. This guide explores the process, from raw material preparation, specific welding methods, including Plasma Arc Welding (PAW) and Tungsten Inert Gas (GTAW) welding, and the comprehensive Radiographic Testing (RT), through to environmental considerations.
Initially, the raw material, primarily stainless steel, undergoes cleaning, polishing, and degreasing to eliminate impurities. The steel is then uncoiled, leveled, and cut according to the pipe specifications. Subsequently, a series of rollers shapes the steel sheet into a cylindrical form, a process known as cold forming.
The welding method used significantly influences the pipe's properties. MTSCO factory utilizes a combination of PAW and GTAW, ensuring high-precision and quality welds.
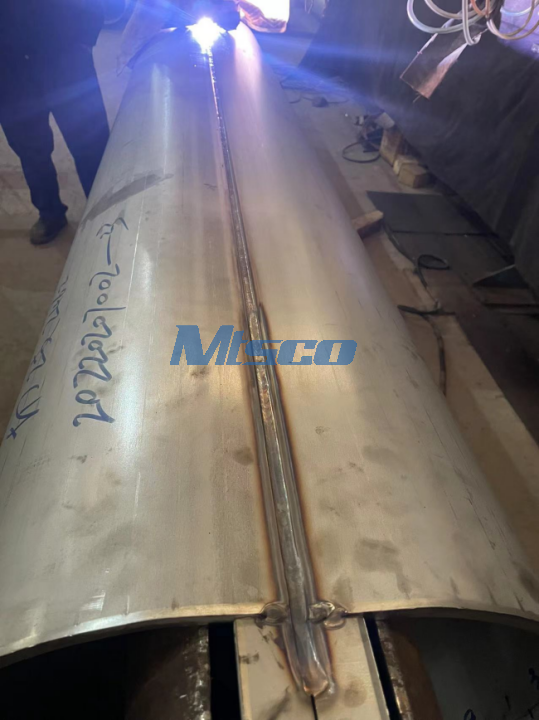

PAW involves a constricted arc between a non-consumable electrode and the workpiece, with an outer shielding gas envelope. This process offers excellent control over the weld, making it suitable for thin materials and complex shapes.
GTAW, or TIG welding, provides a high level of precision. While it's slower and requires more skill than some other methods, it's ideal for welding thin materials and yields a high-quality finish. The combined use of PAW and GTAW allows us to leverage the benefits of both methods, ensuring superior quality and strength in our welded pipes.
Post-welding, the pipe undergoes several finishing processes. Cleaning removes any residual slag or contaminants, while annealing, a heat treatment process, relieves stresses induced by welding. The pipe is then sized, straightened, and prepared for testing.
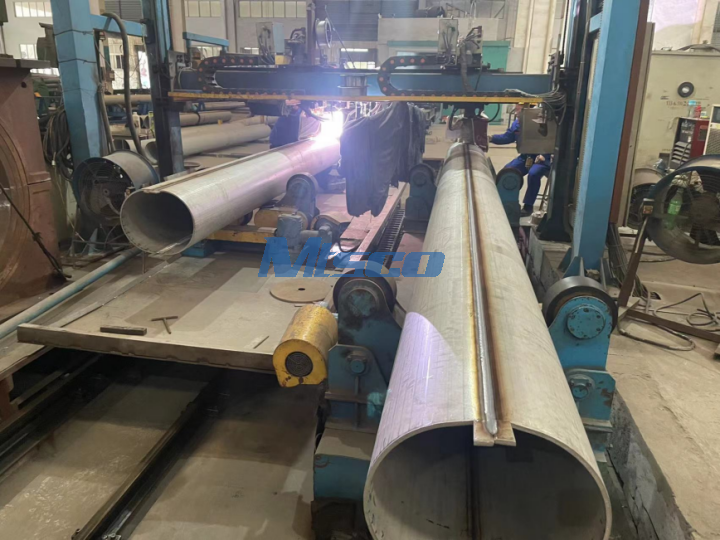

Given the critical nature of the weld in pipe integrity, our factory conducts a 100% Radiographic Testing (RT) on the weld seams. RT is a non-destructive testing method that uses X-rays or gamma rays to view the weld's internal structure and detect any hidden defects. This thorough inspection ensures the highest quality and safety standards in our pipes.
Finally, the pipe is cut, beveled, and given a final inspection before packaging and shipping.
The environmental impact of pipe production is significant, involving substantial raw material and energy consumption and the emission of pollutants. To mitigate these impacts, we enhance energy efficiency, use cleaner energy sources, recycle scrap material, and apply pollution control technologies.

In conclusion, welded pipe production is a demanding process that requires high technical expertise. Each step, from raw material preparation to final inspection, is critical in ensuring the finished product meets required specifications and standards. Prioritizing quality control and environmental sustainability remains a key focus in our modern manufacturing processes.

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
