How are all kinds of metals formed? More than a dozen ways to know it
01 Casting
Liquid metal is poured into the mold cavity which is suitable for the shape and size of the part, and then cooled and solidified to obtain the blank or part, which is usually called liquid metal forming or casting. Casting can be divided into sand casting, investment casting and pressure casting.
Process flow: liquid metal → mold filling → solidification shrinkage → casting
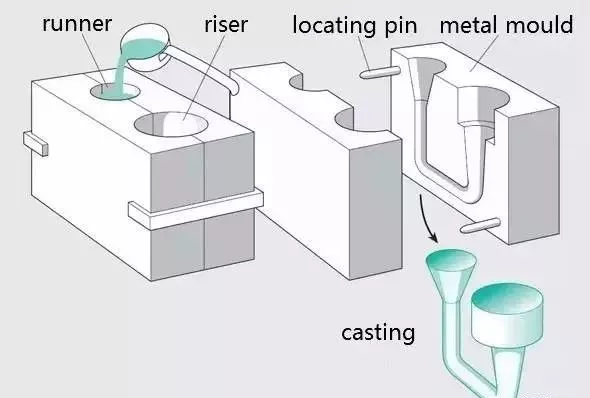
Process features:
It can produce any complex shape parts, especially those with complex cavity shape
Strong adaptability, unlimited alloy types and almost unlimited casting size
There are more than ten casting methods:
Sand casting, investment casting, die casting, low pressure casting, centrifugal casting, gravity die casting, vacuumdie casting, squeezing die casting, Lost foam casting, continual casting,
02 Plastic Forming
Plastic forming: is the use of material plasticity, in the tool and mold under the action of external force processing parts less cutting or no cutting process. It has many kinds, mainly including forging, rolling, extrusion, drawing, stamping and so on.
(1) Forging
Forging: it is a kind of processing method that uses forging machine to exert pressure on metal blank to produce plastic deformation, so as to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, shape and size.
According to the forming mechanism, forging can be divided into free forging, die forging, ring rolling and special forging.

Process flow: forging billet heating → roll forging billet preparation → die forging forming → trimming → punching → correction → intermediate inspection → forging heat treatment → cleaning → correction → inspection
Technical features:
The quality of the forging is higher than that of the casting, and it can bear greater impact force. The plasticity, toughness and other mechanical properties of the forging are also higher than those of the casting, even higher than those of the rolled piece
Raw material saving and processing time reduction
High production efficiency
Free forging is suitable for small batch production of single piece, with great flexibility
Application:
Roll and herringbone gear of large rolling mill, rotor, impeller and retaining ring of steam turbine generator set, huge hydraulic press cylinder and column, locomotive shaft, crankshaft and connecting rod of automobile and tractor, etc.
(2) Rolling

Rolling: it is a pressure processing method that the metal blank passes through the gap (various shapes) of a pair of rotating rollers, and the cross section of the material is reduced and the length is increased due to the compression forming and rolling of the rollers.
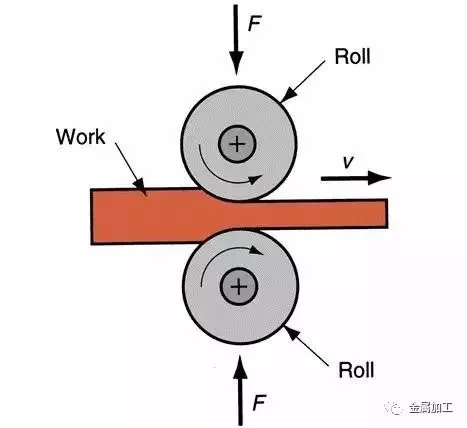
Application: mainly used in metal materials, profiles, plates, pipes, and some non-metallic materials, such as plastic products and glass products.
Most of our stainless steel and nickel alloy pipes are rolled
(3) Extrusion
Extrusion: under the action of three-dimensional non-uniform compressive stress, the blank is extruded from the hole or gap of the die to reduce its cross-sectional area and increase its length. The processing method of the required product is called extrusion. This processing of the blank is called extrusion forming.
Process flow: casting rod heating → extrusion → stretching, twisting and straightening → sawing (sizing) → sampling and inspection → packing and warehousing
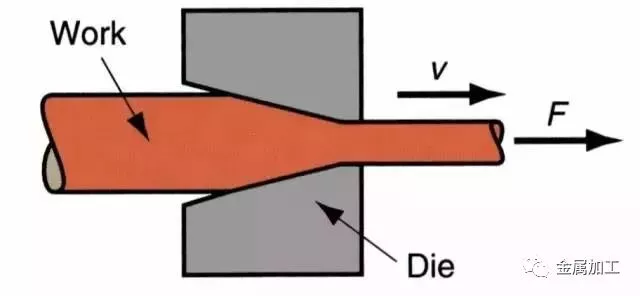
(4) Drawing
Drawing: it is a kind of plastic processing method that uses external force to act on the front end of the metal to pull the metal blank out of the die hole which is smaller than the cross section of the blank, so as to obtain the corresponding shape and size of the product.

Advantage:
·Accurate size and smooth surface
·Simple tools and equipment
·Continuous high-speed production of long products with small cross-section
Disadvantages:
·The pass deformation and the total deformation between annealing are limited
·Limitations on length
Scope of application: drawing is the main processing method of metal pipe, bar, profile and wire.
(5)Stamping

Stamping: it is a kind of forming and processing method to produce plastic deformation or separation by applying external force to plate, strip, pipe and profile by press and die, so as to obtain the workpiece (stamping part) with required shape and size.
Scope of application:
In the world's steel, 60-70% are plates, most of which are made into finished products by stamping. Car body, chassis, fuel tank, radiator, boiler drum, container shell, motor, electrical iron core, silicon steel sheet, etc. are stamping processing. There are also a large number of stamping parts in instruments, household appliances, bicycles, office machinery, household utensils and other products.
Next week, I'll take you to six other metal forming methods

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
