What is Penetrant Testing?
Penetrant testing (abbreviated as PT) is a nondestructive testing method for inspecting surface opening defects based on the principle of capillary action. This method is one of the five conventional nondestructive testing methods and is a comprehensive science and technology.
Like other nondestructive testing methods, penetrant testing is also based on the premise of not damaging the service performance of the tested object, and using the theories of physics, chemistry, material science and engineering to effectively test various engineering materials, parts and products, so as to evaluate their integrity, continuity, safety and reliability. Penetrant testing is an important means to realize quality control, save raw materials, improve technology and provide labor productivity in product manufacturing. It is also an indispensable means in equipment maintenance.
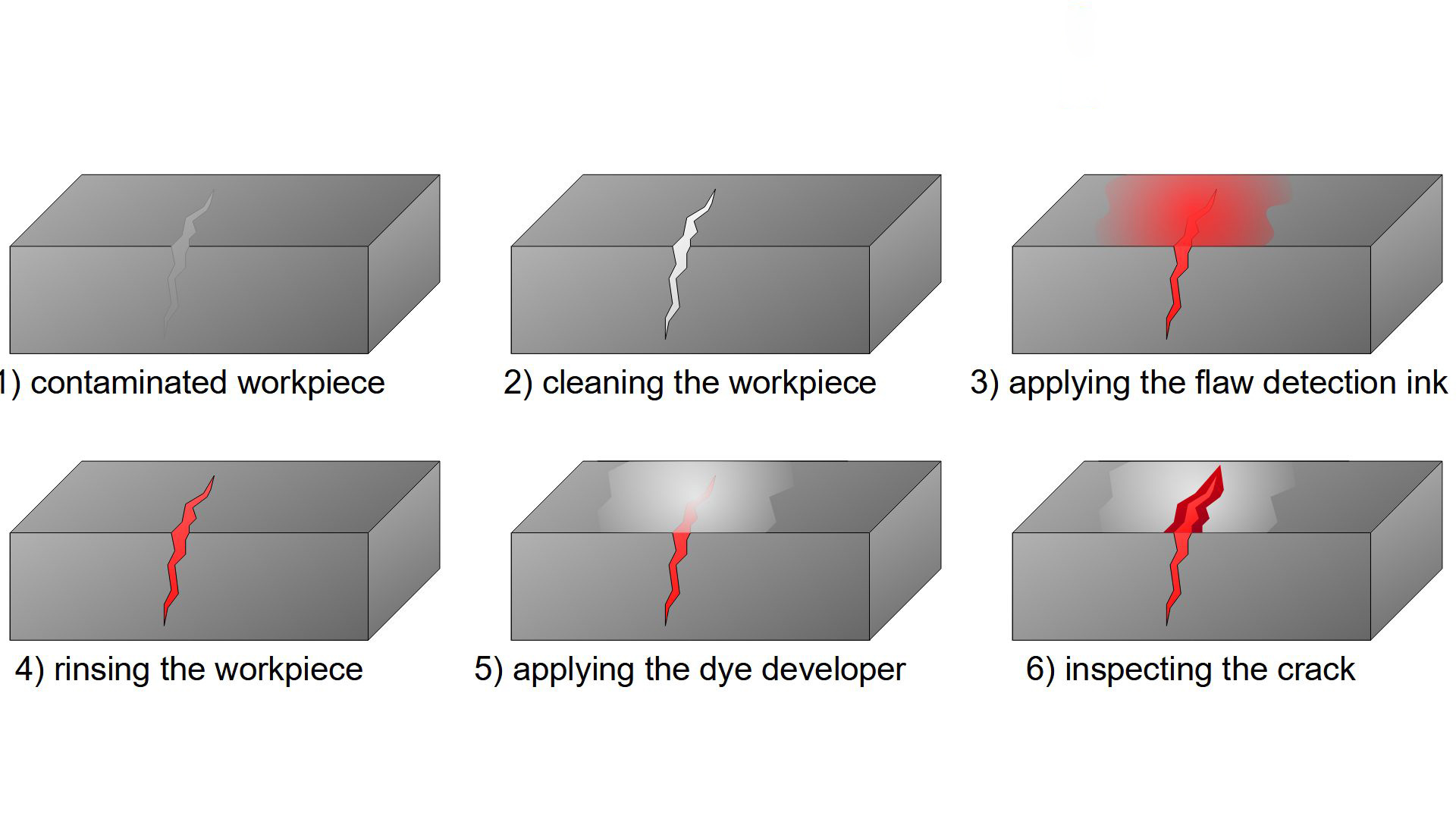
Penetrant testing can be widely used to detect the surface opening defects of most non absorbent materials, such as steel, non-ferrous metals, ceramics and plastics. It can also be used to comprehensively detect the defects with complex shapes at one time. It is mainly used to detect cracks, white spots, looseness, inclusions and other defects without additional equipment. For on-site detection, portable filling penetrant is often used, including penetrant, cleaning agent and developer, which is convenient for on-site use.
The working principle of penetrant testing is: after the workpiece surface is coated with penetrant containing fluorescent dye or colored dye, under the action of capillarity, the penetrant can penetrate into the surface opening defect after a certain time; Remove the excess penetrant on the surface of the workpiece, dry it, and then apply the adsorption medium developer on the surface of the workpiece; Similarly, under the capillary action, the developer will attract the penetrant in the defect, that is, the penetrant will seep back into the developer; Under a certain light source (black light or white light), the penetrant trace at the defect is displayed (yellow green fluorescence or bright red), so as to detect the morphology and distribution of the defect.
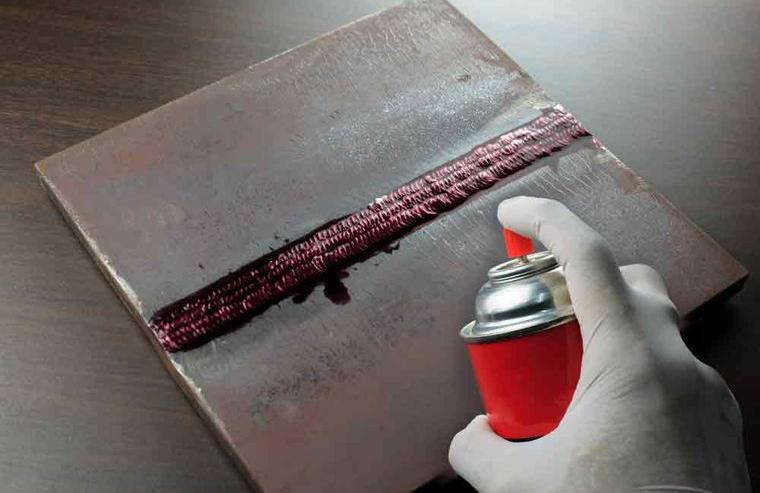

The results of penetrant testing are mainly affected by the operation of the operator, so the personnel conducting penetrant testing must operate in strict accordance with the relevant process standards, procedures and technical requirements, so as to ensure the reliability of the test results.

 English
English 中 文
中 文 Español
Español Português
Português Deutsch
Deutsch Türk
Türk Pусский
Pусский عربي
عربي 한국인
한국인 日本語
日本語
